Page 15 - GUIDELINES FOR FOOD SYSTEMS ISSUES PRIORITIZATION, ACTOR AND ACTION MAPPING at sub-national levels in Vietnam
P. 15
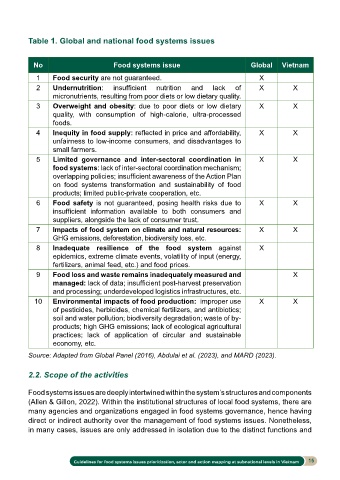
Table 1. Global and national food systems issues
No Food systems issue Global Vietnam
1 Food security are not guaranteed. X
2 Undernutrition: insufficient nutrition and lack of X X
micronutrients, resulting from poor diets or low dietary quality.
3 Overweight and obesity: due to poor diets or low dietary X X
quality, with consumption of high-calorie, ultra-processed
foods.
4 Inequity in food supply: reflected in price and affordability, X X
unfairness to low-income consumers, and disadvantages to
small farmers.
5 Limited governance and inter-sectoral coordination in X X
food systems: lack of inter-sectoral coordination mechanism;
overlapping policies; insufficient awareness of the Action Plan
on food systems transformation and sustainability of food
products; limited public-private cooperation, etc.
6 Food safety is not guaranteed, posing health risks due to X X
insufficient information available to both consumers and
suppliers, alongside the lack of consumer trust.
7 Impacts of food system on climate and natural resources: X X
GHG emissions, deforestation, biodiversity loss, etc.
8 Inadequate resilience of the food system against X
epidemics, extreme climate events, volatility of input (energy,
fertilizers, animal feed, etc.) and food prices.
9 Food loss and waste remains inadequately measured and X
managed: lack of data; insufficient post-harvest preservation
and processing; underdeveloped logistics infrastructures, etc.
10 Environmental impacts of food production: improper use X X
of pesticides, herbicides, chemical fertilizers, and antibiotics;
soil and water pollution; biodiversity degradation; waste of by-
products; high GHG emissions; lack of ecological agricultural
practices; lack of application of circular and sustainable
economy, etc.
Source: Adapted from Global Panel (2016), Abdulai et al. (2023), and MARD (2023).
2.2. Scope of the activities
Food systems issues are deeply intertwined within the system’s structures and components
(Allen & Gillon, 2022). Within the institutional structures of local food systems, there are
many agencies and organizations engaged in food systems governance, hence having
direct or indirect authority over the management of food systems issues. Nonetheless,
in many cases, issues are only addressed in isolation due to the distinct functions and
Guidelines for food systems issues prioritization, actor and action mapping at subnational levels in Vietnam 15